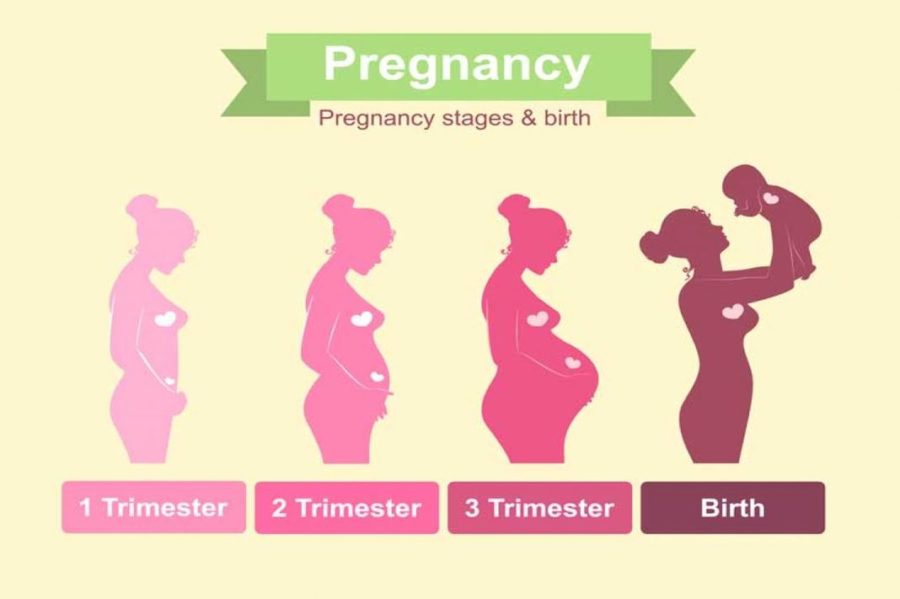
Pregnancy leads to a range of body changes. These may go from regular and anticipated changes to less common changes, like swelling and fluid retention, and changes in vision. Read on to know week by week body changes during pregnancy.
Physical Changes During Pregnancy
Some women will automatically tell you they know when they become pregnant. All of us are familiar with common symptoms: no period, nausea, vomiting, aversions to food. Physical changes that occur in the body of a woman are the primary markers of deciding whether or not she is pregnant. If you are pregnant you must have had the symptoms listed below. But if you did not then we’re suggesting to lookout these changes. These changes are clear signs of pregnancy, especially when you have never seen them before!
1. Missed period
Missed period is one of the most noticeable signs of pregnancy. While a woman with irregular menstrual cycles may present a deceptive symptom, a missed period also means that she is pregnant. If in spite of the specified period since your last period, your menstrual cycle has not yet started, you may be pregnant.
2. Tender And Swollen Breast
Another symptom of pregnancy is sensitive breasts with soreness and mild pain. Uncomfortable conditions arise from hormonal changes within the body and decrease gradually over time.
3. Nausea
At any time of the day or even at night, nausea will occur. Nausea can start as early as two weeks after conception, for pregnant women. Also, a pregnant woman can have an enhanced sense of smell.
4. Frequent urination
When the baby continues to develop in the womb, the pressure on the bladder and uterus rises. That leads to frequent bathroom trips.
5. An increased fatigue
A pregnant woman can feel exhausted and dizzy as well. A woman may also faint in the early stages of pregnancy due to low blood sugar.
6. Breathlessness
Another common symptom of pregnancy is breathlessness or shortness of breath.
Although the common symptoms described above may be signs of other health problems or problems in the body when you experience a combination of these symptoms at the same time, you may be pregnant and this is when you need to take a home pregnancy test to confirm if you have not already.
Week By Week Body Changes During Pregnancy
Your due date is determined on the day of the last menstrual cycle. Your body will be getting ready to deliver the baby in just 40 weeks. Let’s look at week by week body changes during pregnancy.
1. Week 1
You’re not pregnant at all if you’re 1 week pregnant! From week 1 to week 2, the sperm enters the egg. In general, the beginning of the pregnancy is usually week 1 from the due date. At this time one of the two ovaries matures and releases an egg. If both ovaries release eggs, non-identical twins will bear on them. This is the week you begin to take your prenatal vitamins. This week, the egg is swept into the Fallopian tube and follows the Fallopian tube and awaits sperm to come.
Also Read 1-week pregnant
2. Week 2
Ovulation takes place during week 2. The best time to have intercourse to enhance the chances of a successful pregnancy is two or three days before the second week. If the glands produce estrogen and progesterone, the breasts begin to glow, triggering hormone surges and tender breasts.
Also Read 2-weeks pregnant
3. Week 3
Finally, the sperm enters the egg and is reached by 200 million competitors. At this point the egg becomes the zygote and shuts down, stopping it from entering by other sperms. Although physical changes aren’t immediate, there are certain changes at this point on a biological basis. The nuclei fuse with the zygote and give it its gender and genetic characteristics, including eye color, hair color, and other common genetically determined characteristics among 200 others.
Also Read 3-weeks pregnant
4. Week 4
At this stage, bodily changes that develop in the first month of pregnancy start to manifest. Any of the changes in the body during early pregnancy include swollen and sore breasts, fatigue, frequent urinating urge, and nausea. Placenta and umbilical cord development starts, and the fertilized egg will reach into the uterus and exert pressure, allowing it to lose a few drops of blood. Testing can be performed after a week as false-negatives are usual where research takes place on the very first day of the menstrual period ends.
Also Read 4-weeks pregnant
5. Week 5
The embryo starts forming and develops into the size of a grain. From this week’s modifications and growth of the embryo’s brain, organs, and blood vessels take place. On the baby’s back a groove form that binds itself to create the neural tube, which then becomes the baby’s spinal cord.
Also Read 5-weeks pregnant
6. Week 6
The neural tube transforms into the spine and the heart is starting to pump more blood. The embryo’s C-shape is becoming more pronounced and you might be prone to fatigue and tiredness. The variations in hormone levels will also cause blood pressure to drop. The embryo becomes encircled by a protective membrane and connected to the yolk sac. Exercising will allow you to deal with stress and offer some relief. Pregnant women continue to be given adequate folic acid at this time. It is very important to the spinal cord and brain development of the fetus. Deficiency of folic acid can cause serious birth defects, such as neural tube defects.
Also Read 6-weeks pregnant
7. Week 7
Morning sickness is getting worse by this time and the embryo’s brain and face tend to develop and form. The baby’s eye lenses grow, nasals grow and the arms start to look like a paddle. Mucus thickens at the cervix and secures the womb entrance. The fetus starts displaying fingers and toes and manifestations of brainwave movements. You’re going to experience mood swings and sickness. This is a positive indicator that the hormones in your pregnancy are in motion.
Also Read 7-weeks pregnant
8. Week 8
Brainwave actions are marked at the beginning of the 8th week in the embryo. When you stand, the pelvis will feel intense pain. Using ultrasound scans, the doctor tests for signs of heartbeat or embryo development. When the fetus is confirmed, the probability of abortion decreases to 2%, and from this point on, a formal due date is given. You could have bleeding during the first trimester of your pregnancy.
9. Week 9
The embryo develops at 9 weeks and you may feel squeezed on the bladder as a result. This could lead to urinary leakage. The heart and the eyelids of the child will grow during this time. He’ll develop his hair follicles and nipples too. Your infant won’t be an egg anymore, he’ll be a fetus. The 9th pregnancy week is a vital time for the growth of the arm and leg. Your little one is still developing with a liver, gallbladder, spleen, and adrenal gland. The baby may inhale or exhale amniotic fluid when the baby’s respiratory system is developing, which may lead to hiccups that are important to the production of healthy diaphragms. But for a few more months you won’t be able to really experience the fetal hiccups. You may feel dehydrated – it’s important that you drink lots of water this week because most doctors say it’s probably the roughest period of pregnancy.
10. Week 10
By week 10 almost all the vital organs of your baby will be fully developed and start working. Your baby will be named ‘fetus’ legally. The cartilage and bones of the infant will begin to develop and even the genital will develop. The fetus’ eyes are likely to become more pronounced. The fetus may obtain oxygen via the umbilical cords, and the womb will detect irregular breathing motions.
11. Week 11
The fetus will breathe, suck his thumb and sigh by week 11. During this time the baby’s facial growth begins and the fetus’ head grows wider than the body. During the 11th week, food cravings become noticeable and you may find yourself longing for items contrary to food such as pica, which may suggest a nutritional deficit. It’s necessary to ingest folate, fiber, and iron, and consuming chives will help. Around weeks 11 and 13, the first-trimester ultrasonic scan will be performed to monitor chromosomal anomalies alongside a Nuchal translucency test.
12. Week 12
Your baby will start growing even more now 3 inches in age. Your baby’s face will look more normal and the baby will weigh around half an ounce I.e.around 14gms and crown about 2 to2 1/4 inches rump length; around a lime’s height. The majority of the body will begin to expand, and head development is slow to take the proportions of other areas of the body into account. The stance of the baby will move to a curling and upright pose. You may have trouble getting through the stools. Also, You may have a heart rate and a gassy stomach. You will find your hips growing to fit your uterus’ growing height.
13. Week 13
Your baby and you made it through the first trimester. Congratulations. As you enter the second trimester of your pregnancy, your body changes will change completely. It is necessary from now on to eat healthily and to drink a lot of fluids. You’re going to feel a little happier as morning nausea and vomiting decline. At this point, swimming workouts with low-impact yoga are also prescribed for pregnant women. The baby has fetal hiccups that open up the diaphragm passage and help to breathe. The baby’s kidney function begins, and the bone marrow starts the development of white blood cells to combat different diseases. During this week the pancreas, gallbladder, and thyroid may also develop.
14. Week 14
The baby organ begins to develop and, by ultrasound scans, you can finally see human facial features. The intestine passes into the baby and the development of insulin begins. For the first time, you may feel the kicks of your newborn. Baby movements known as quickening are usually talked from about 16 to 18 weeks, but women who have already given birth have more muscle relaxation and fetal activity can also be detected as early as 14 weeks. Your doctor will prescribe an ultrasound scan during this week to search for neural tube abnormalities such as spina bifida or Edward syndrome in your baby.
15. Week 15
Blood protein screening checks and Down syndrome symptoms or developmental abnormalities at this phase are performed. Female fetuses exhibit more mouth movements than males. The weight of the fetus is about 5 inches and weighs 2 ounces. Near the belly button, a small hump emerges. Braxton-Hicks contractions can also be found in the uterus. Contact a doctor for more than 4 contractions every hour and if mucus discharge in the vagina is painful and regular.
16. Week 16
A spurt of development starts with the forming of the bone. During the rest of your pregnancy, you may get a pound per week, i.e. about 0.454 kg per week. Your pelvic area feels hard and strong. You will likely see signs that by this point your baby’s expression has become more pronounced.
17. Week 17
You will have vivid, sometimes disturbing dreams. This reflects the overall normal anxiety or fears around birth and parenthood. The baby is going to weigh more than the placenta by this time. The brown fat that produces heat in the baby’s body is stored. Your breasts can become soft, delicate, and often even dull. The glow of pregnancy, which is an indication of improved blood supply, is also seen on your face. From this week to week 22, the baby’s first kicks are usually heard. The placenta now functions absolutely. It consumes nutrients and distributes them during waste disposal.
18. Week 18
There will be more ultrasound scans to assess the baby’s gender here. You will not be notified by the doctor, however. The baby can respond to such stimuli. Fluttery kicks can be noticed more. The retina of the baby would become light and sensitive. The kid will walk around and even cross his legs. Often continue to grow teeth and fat deposition. Sorrows can also be found in the arm, tailbone, and other muscles.
19. Week 19
Ultrasound scans of your baby growing show pictures of your baby holding the amniotic bag membrane, sucking thumbs, or going into the womb. If your baby is a female, the development of follicles inside your body begins at this point, with half the genetically modified material produced in it. Make sure you eat food high in B-vitamins and good fats because it helps your baby grow his brain.
20. Week 20
Your uterus will rise to 1 centimeter a week in your rib cage. This is the moment that mothers attend childbirth classes and practice strategies and relieve discomfort and glide into the system easily. Since you are halfway there to give birth to a baby, your outlook will improve greatly. Immunities from the uterus are transferred into the fetus.
21. Week 21
You should be a bit concerned about how your body can adjust while you are pregnant when you’re 35 years old or older, or when you have diabetes and other chronic conditions. Since the third trimester of pregnancy, symptoms of eclampsia risk show. To avoid these problems, you can take walks and rest every day.
22. Week 22
You’re in your 5th month of pregnancy. At week 22, the brain of your baby grows quickly and you will feel hemorrhage or constipation. Yeast infections around the vagina, and repeated vaginal discharges during this period, are typical symptoms throughout the body. Douching is alert and redness, itchiness, and yeasts are labeled for the vaginal fluid. The baby’s organs mature and a variety of other nutrients are provided by the blood that flows through the umbilical cord.
23. Week 23
The eyes of your baby will develop by now but there will be no color due to the lack of pigmentation. Your doctor can warn you against long-distance driving or traveling not because it’s dangerous, but just to make sure they’re able to support you if you’re going to labor.
24. Week 24
During this week your body will get heartburn. The heartburn symptom is similar to growing hair on your baby’s head. You can find your child bald if you don’t experience heartburn. Muscle aches, swollen muscles, tiredness, and dizziness are other changes in the body that can occur this week.
25. Week 25
Exercise is important to boost the regeneration process after birth from this point forward. Your baby is going to get a regular cycle of sleep and open his nostrils. Inflation helps the baby’s lungs develop a surfactant that allows the small air sacks inside the lungs to breathe better. Back, hip, and leg pain can be found in the body. During this period, exhaustion and dizziness can resurface.
26. Week 26
During this time, the baby’s hearing system develops and responds to noise. During your sleep, you can feel discomfort. Sleep on your side instead of the back, since lying on the back prevents the blood flow through your baby because the uterus sits over a major artery. You can see stretch marks in the belly.
27. Week 27
You are in the third trimester of pregnancy and you should be able to cope with back pain. You can experience a lot of back pain during this time. Shooting pain called sciatica can occur. The pressure and amniotic fluid concentrations are reduced by walking, bending, and walking. When the baby moves, the point ends with the toes and knees or, sometimes, the bony edges can be seen. You can raise your heart rate and feel flushed.
28. Week 28
Be prepared to feel Braxton-Hicks contractions around the abdomen when you are in the third trimester of your pregnancy which is essentially a contracting muscle feeling in the abdomen. The pace at which you gain weight will raise and the amount of body fat in the baby will rise to 2 or 3 percent. Stop staying in hot weather for too long or for extended stretches of time as it will make you feel dizzy. You may have low blood pressure, as well. Drink lots of water and if you are pregnant during summer don’t go out too much. Your abdomen will still increase in size so the body will feel bloated. Even at this time, you may anticipate ache and leg cramps.
29. Week 29
The 29th week is common for regular trips to the bathroom and napping. The breathing system and organ functions of your infant are now completely formed and need no respiratory support. Prolactin is rising and the breasts are beginning to secrete colostrum. The baby develops estriol from the adrenal glands.
30. Week 30
Your uterus will keep on expanding and start crowding your diaphragm. You could feel breathless. Breathing problems and discomfort will lead to repeated urination on your bladder. Your maternity classes should begin, and they should finish around week 36.
31. Week 31
The area in your belly will diminish as your baby grows and your bowels get even larger. Ten kicks per hour signify a good baby growth rate in the fetus and doctors appoint people to keep track of the movements of the infant. If inactivity is found drink a glass of fresh, raw fruit or vegetable juice.
32. Week 32
By now, the five senses of your baby will grow entirely. Your baby will undergo REM periods during sleep and its breathing patterns will be increased within your womb and will thus prepare to join the world.
Also Read 32-weeks pregnant
33. Week 33
The position of the infant becomes head-down so that it is primed for the birth movements. This position also brings his brain more oxygen which will induce more abdominal contractions.
Also Read 33-weeks pregnant
34. Week 34
When the light is on the stomach, the pupils respond and enlarge and constrict. During this week, your baby will sleep a lot inside your womb as his brain constantly grows. The infant will also have more complex REM periods while dreaming and may also have hallucinations.
Also Read 34-weeks pregnant
35. Week 35
Your infant height is about 16 to 20 inches in size and is ready for delivery. During this time, the nervous and immune systems of the infant develop, and your kid’s weight can be noticed. You can have to take breaks to hang around or do regular daily activities for brief periods. Owing to the existence of GroupB Streptococcal, bacteria that reside in the vagina and are capable of transmitting infections on to the infant, you will be screened for the next two weeks from 35 Days. The procedure normally consists of a soft rub with a cotton swab in the rectum.
Also Read 35-weeks pregnant
36. Week 36
The motions of your baby should now settle down and the actions of your fetus can be seen about 20 times every day. You should drink a glass of orange juice and lay on your side when you are worried. This helps the child to get up and move for a while.
Also Read 36-weeks pregnant
37. Week 37
Meconium is formed by the baby’s intestines. It helps with his first bowel movement as soon as they get out of labor. The fetus currently is around 20 to 21 inches in height and the infant is around 2.7- 3.1 kilograms, i.e. 6 to 7 pounds. In anticipation of the birth, your baby may already begin to breathe. Your breasts leak colostrum that is a food supply for your baby that can help your abdomen feel a bulge.
Also Read 37-weeks pregnant
38. Week 38
At this time, the lanugo, which is the hair on your baby’s body, will go away. Your baby will be completely developed by now; however, associations will begin to build in the brain that will occur long after childbirth. The nails of your baby can ripen and meet the fingers and toes end. Sometimes pain in the back and neck is normal. Reduced mobility is also normal, and the increased exhaustion can be challenging for you. Get fast relief with small, but often healthy meals.
Also Read 38-weeks pregnant
39. Week 39
The height of your infant is currently 6 to 10 pounds or around 2.7 to 4.5 kilograms, and about 17 and 23 inches. Your baby starts to develop neural connexions and has internal hair development and weight gain. A few weeks before you join last week, you might consider taking maternity leave. Relax, go for a movie, and stretch your hands and knees together with exercises of pelvic tilting to get relaxation.
Also Read 39-weeks pregnant
40. Week 40
Your baby will be ready for birth at week 40, from this week on. If your baby has not yet been born because you have not been going to labor this week, doctors will be watching you for another two weeks. At this point, pregnancies close; but, if it persists, it is considered ‘post-dated.’ Your labor-date is coming soon and you’ll have your baby in your arms.
Also Read 40-weeks pregnant
41. Week 41
When your baby has not yet been delivered, the doctor will recommend initiating labor. If the pregnant woman does not go into labor by week 42, it is considered dangerous for both the mother and the baby.
Also Read 41-weeks pregnant
42. Week 42
When the infant has not yet been delivered, the doctor will cause labor, indicating either a C-section or a vaginal delivery. If the cervix has not weakened, the doctor can manually trigger contraction by injecting hormones to strengthen the cervix for the birth of the infant. Procedures such as scraping the membranes and splitting them apart are used. Popular labor induction approaches require the use of medications such as oxytocin to induce vaginal contractions. If considering the manual labor induction process, vaginal contractions do not occur, you will require a C-section operation to deliver the infant.
Also Read 42-weeks pregnant
So, these are week by week body changes during pregnancy.
It is crucial to promote recovery once your baby is born, by improving your diet, exercise, and nutrition. It is advised to stop smoking, tobacco use, and avoidance of alcohol intake before you get pregnant, particularly before week 1 to improve the chances of a healthy pregnancy and a problem-free delivery.
Also Read: Important Pregnancy Care Tips During Monsoon