What Are Thyroid Disorders?
The thyroid gland affects nearly all the metabolic processes in your body via the hormones it produces. Thyroid disorder can range from a small, harmless goiter (large gland) to life-threatening cancer that does not need any treatment. The most common thyroid issues involve abnormal thyroid hormone production. Too much of the thyroid hormone leads to a hyperthyroidism condition. Insufficient production of hormones results in hypothyroidism.
While the effects may be unpleasant or uncomfortable, if properly diagnosed and treated, most thyroid problems can be handled well.
Causes Of Thyroid Disorder
The following is a list of some common thyroid disorder.
1. Hyperthyroidism:
Too much thyroid hormone is called overactive thyroid gland hyperthyroidism because it speeds up body metabolism. This hormone imbalance occurs in about 1% of all women who are more likely to get hyperthyroidism than men. The disease of Graves is one of the most common forms of hyperthyroidism. This autoimmune disorder tends to run in families (when your body’s defense system attacks your own cells). Because in hyperthyroidism, the thyroid gland produces too much hormone, the body develops an increased metabolic state, with abnormal function in many body systems.
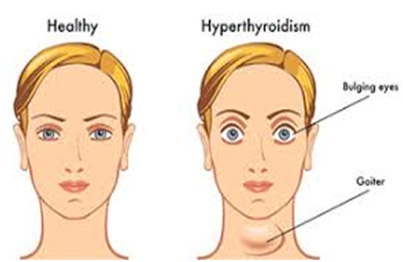
Image Source – Holy Basil Mediclinic
2. Hypothyroidism:
Too little thyroid hormone is called underactive thyroid gland hypothyroidism. In hypothyroidism, the body’s metabolism is slowed down. There are several causes, most of which directly affect the thyroid gland, impairing its ability to make enough hormone. More rarely, a pituitary gland tumor may occur that prevents the pituitary from producing TSH. Whether this problem comes from the thyroid or from the hypophysis, the consequence is that the thyroid produces too little hormones that slow down many physical and mental processes. The body consumes less oxygen and generates less heat from the body.
3.Thyroid Nodules:
A thyroid nodule in the thyroid gland is a small lump. It is common to have thyroid nodules. The thyroid tissue or the fluid-filled cyst that forms an injection into the thyroid gland can develop as these nodules. Almost half the population have tiny thyroid nodules at some stage in their life, but normally they are not visible as long as they get big and affect ordinary thyroid sizes. Roughly 5% develop larger nodules (approximately 1 centimeter), more than a half inch across.
Although most nodules are not cancerous, people who have them to rule out cancer should seek medical assistance. Some thyroid nodules can also generate too much thyroid hormone, cause hyperthyroidism or become too big, interfere with breathing or swallowing or cause pain in the throat.
Other issues
Other issues with thyroid include cancer, thyroiditis (thyroid gland inflammation), or goiter, which is a thyroid gland enlargement.
Diagnosis Of Thyroid Disorder
Due to the easy confusion of symptoms with other conditions, thyroid illness can be difficult to diagnose. Luckily, a test, called the thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) test, can recognize thyroid disorders even before symptoms begin. The American Medical Association’s Journal discovered that screening for mild thyroid failure in males and females over 35 years of age is as cost-effective as screening for more prevalent issues such as high cholesterol or high blood pressure.
Treatment can control the disorder even before symptoms start when thyroid disease is caught early.
Treatment Of Thyroid Disorder
The objective of any thyroid disorder therapy is to restore ordinary thyroid hormone blood concentrations.
Hypothyroidism is treated with levothyroxine. This is a synthetic tablet of hormones that replaces the body’s missing thyroid hormone. Your doctor will adjust your dosage accordingly with thorough surveillance, and you will be able to return to your ordinary lifestyle quickly.
Hyperthyroidism, which is usually harder to treat, needs thyroid hormone production to be normalized. Treatment may require drug therapy to prevent the development of hormones, radioactive iodine treatment that disables thyroid surgery, or even thyroid surgery to remove some or all of the gland.
Radioactive iodine is the most common therapy. This treatment usually leads to hypothyroidism that requires the utilization of levothyroxine to restore normality.
Thyroid diseases are conditions that last for a lifetime. People with thyroid disease can live a good, ordinary life with careful management.
In most instances, thyroid illnesses are not life-threatening and can be well managed with medical therapy. Some circumstances may need surgery. The outlook for most individuals with thyroid cancer is also good, although there is a poorer prognosis for patients with thyroid cancer that has spread across the body.
Also Read: Breast Cancer – Symptoms And Causes